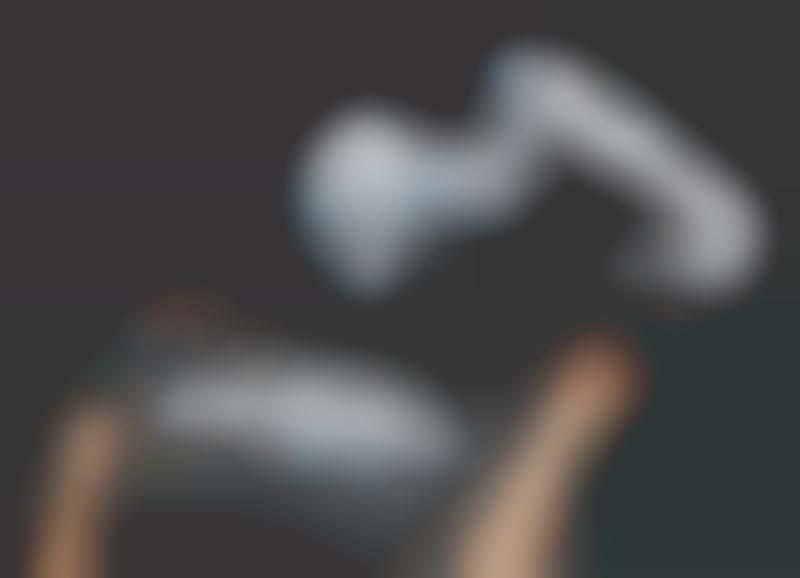These Robotic Arms Can Teach Itself to Carry Out Tasks
Rahul Kalvapalle — March 11, 2019 — Tech
References: festo & machinedesign
The BionicSoftHand is an innovative robotic limb that is designed to offer an upgrade on existing robotic arms by virtue of its ability to blend the tactile advantages of a soft structure with the stability and durability of harder materials.
Developed by Festo, the BionicSoftHand robotic limb is sheathed in a special silicone layer, with the fingers of the arm made of a flexible substance. This setup makes it possible for the arm to bend safely and gently.
In addition to its structural benefits, this robotic limb also has the additional advantage of being able to teach itself how to perform tasks, using a combination of artificial intelligence and embedded cameras to analyze assigned tasks and perform them.
Flexible, durable and intelligent, this robotic limb offers promise for a range of industrial and scientific applications.
Developed by Festo, the BionicSoftHand robotic limb is sheathed in a special silicone layer, with the fingers of the arm made of a flexible substance. This setup makes it possible for the arm to bend safely and gently.
In addition to its structural benefits, this robotic limb also has the additional advantage of being able to teach itself how to perform tasks, using a combination of artificial intelligence and embedded cameras to analyze assigned tasks and perform them.
Flexible, durable and intelligent, this robotic limb offers promise for a range of industrial and scientific applications.
Trend Themes
1. Soft Robotics - The use of soft materials to create robotic limbs offers flexibility and safety advantages while maintaining stability and durability.
2. Self-teaching Robotics - Robotic limbs that can analyze tasks and teach themselves how to perform them offer a significant opportunity for automation.
3. Intelligent Robotics - Artificial intelligence and embedded cameras enable robotic limbs to analyze complex tasks and make decisions in real-time, providing new possibilities for automation.
Industry Implications
1. Manufacturing - Soft robotics can be used to improve automation, safety, and precision in manufacturing, leading to more efficient production processes and cost savings.
2. Healthcare - Soft, flexible robotic limbs can be used to create prosthetics that more closely mimic the motion of natural limbs, providing greater mobility and independence for patients.
3. Agriculture - Self-teaching and intelligent robotic limbs can be used to improve crop harvesting processes, reducing labor costs and increasing efficiency in the agriculture sector.
0.8
Score
Popularity
Activity
Freshness